Email: [email protected] Phone: (+86) 134 1323 8643
Installation and Configuration of a CNC Zero Probe
Ensuring Precise Workpiece Positioning in CNC Machining
The CNC zero probe is indispensable for achieving precise workpiece positioning and maintaining consistent part quality in CNC machining operations. Its correct installation and configuration are vital for optimizing its functionality and enhancing machining efficiency.
Selecting the Optimal Location for the Zero Probe
Installing a CNC zero probe requires careful consideration of its physical location and secure electrical connections. The probe must be mounted on a stable and rigid structure to minimize vibrations and ensure precise measurements. Additionally, the mounting location should be easily accessible to the CNC machine’s tool change mechanism for smooth tool exchanges.
Configuring the Zero Probe in the CNC Control System
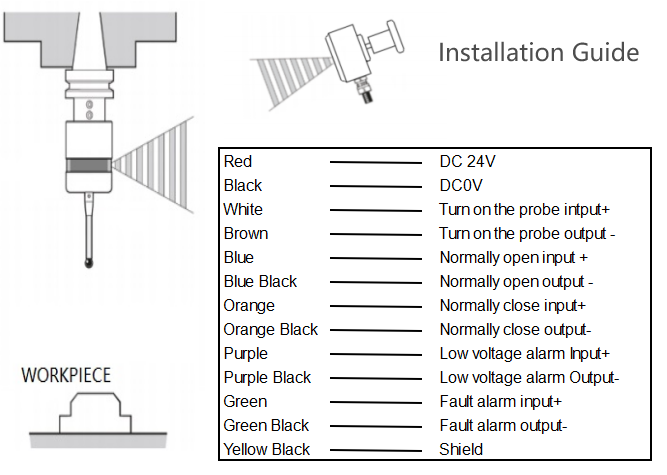
After installing the zero probe physically, the next step is to configure it within the CNC control system. This involves assigning the correct inputs and outputs to the probe’s signal wires and adjusting the control parameters to ensure accurate triggering and reliable surface detection.
Ensuring Reliable Electrical Connections
The electrical connections for the zero probe must adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications. Proper grounding and shielding are essential to minimize electrical noise and ensure accurate signal detection. The connections should be tight and secure to prevent any loose or faulty contacts, which could compromise the probe’s performance.
Calibrating the Zero CNC Probe for Accurate Measurements
Once the physical and electrical installations are complete, calibrating the zero probe is necessary to ensure its accuracy. This involves running a test cycle where the probe is manually triggered against a known reference surface, and then adjusting the control parameters to ensure the CNC machine correctly recognizes the workpiece surface.
Integrating the Zero Probe into Tool Change Routines
The final step in the configuration process is assigning the zero probe to the appropriate tool change routine. This step ensures that the machine automatically measures and compensates for the correct tool length each time a tool is changed. The CNC control system should be programmed to initiate the zero probe routine at the start of each machining cycle.
Maximizing Machining Accuracy and Efficiency
By carefully installing, configuring, and calibrating the CNC zero probe, manufacturers can achieve precise workpiece positioning and consistent tool length compensation, leading to improved machining accuracy. The benefits of using a zero probe include increased productivity, reduced setup time, and enhanced part quality
CNC Zero Probe FAQ
1.What is a CNC zero probe and why is it important?
A CNC zero probe is a precision tool used in CNC machining to accurately detect the surface position of a workpiece. This ensures that the CNC machine knows the exact location of the workpiece, which is crucial for accurate machining and maintaining consistent part quality. By precisely locating the workpiece, the zero probe helps in reducing setup times and improving overall productivity.
2.How do I install a CNC zero probe?
Installing a CNC zero probe involves several key steps:
- Physical Mounting: Securely attach the probe to a stable and rigid structure to minimize vibrations and ensure precise measurements.
- Electrical Connections: Connect the probe’s signal wires according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Ensure proper grounding and shielding to minimize electrical noise.
- Positioning: Choose a location that is easily accessible to the CNC machine’s tool change mechanism for smooth tool exchanges.
3.What should I consider when selecting a location for the zero probe?
When selecting a location for the zero probe, consider the following:
- Stability: The probe should be mounted on a stable and rigid part of the machine to prevent vibrations that can affect accuracy.
- Accessibility: The probe should be easily accessible to the CNC machine’s tools for easy exchanges and to facilitate the tool change process.
- Space: Ensure there is enough space for the probe to operate without obstruction.
4.How do I configure a CNC zero probe in the control system?
Configuring a CNC zero probe involves:
- Assigning Inputs/Outputs: Assign the appropriate control system inputs and outputs to the probe’s signal wires.
- Adjusting Control Parameters: Set the parameters in the CNC control system to accurately trigger the probe and detect the workpiece surface.
- Calibration: Run a test cycle to manually trigger the probe against a known reference surface and fine-tune the control parameters for accuracy.
5.Why is proper grounding and shielding important for the zero probe?
Proper grounding and shielding are crucial because they:
- Reduce Electrical Noise: Minimize interference from other electrical components that can cause inaccurate readings.
- Ensure Signal Integrity: Maintain the integrity of the probe’s signals for precise detection and measurements.
- Prevent Damage: Protect the probe and control system from potential electrical faults.
6.How do I calibrate a CNC zero probe?
Calibrating a CNC zero probe involves:
- Manual Triggering: Trigger the probe against a known reference surface to establish a baseline measurement.
- Parameter Adjustment: Adjust the CNC control system’s parameters to align the machine’s recognition of the workpiece surface with the actual probe measurement.
- Testing: Perform multiple test cycles to verify and refine the probe’s accuracy.
- Can the zero probe be integrated with the tool change routine?
Yes, integrating the zero probe with the tool change routine is essential for ensuring accurate tool length compensation. The CNC control system can be programmed to automatically initiate the zero probe routine at the start of each machining cycle. This process helps to automatically measure and adjust for the correct tool length each time a tool is changed.
8.What are the benefits of using a CNC zero probe?
Using a CNC zero probe offers several benefits:
- Increased Productivity: Reduces setup time by quickly and accurately locating the workpiece.
- Improved Accuracy: Ensures precise positioning and tool length compensation, leading to higher machining accuracy.
- Enhanced Part Quality: Consistent and accurate workpiece positioning results in better quality finished parts.
- Reduced Waste: Minimizes errors and material waste by ensuring proper alignment and positioning.
9.What maintenance is required for a CNC zero probe?
Maintaining a CNC zero probe involves:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the probe clean from dust and debris to ensure accurate readings.
- Inspection: Periodically inspect the probe for wear or damage and ensure connections are secure.
- Recalibration: Recalibrate the probe regularly or after any significant changes to maintain accuracy.
10.Are there different types of CNC zero probes?
Yes, there are different types of CNC zero probes designed for various applications and machine setups, including:
- Contact Probes: These physically touch the workpiece to detect its position.
- Non-Contact Probes: Use sensors like lasers or capacitive sensors to detect the workpiece without touching it.
- Optical Probes: Utilize optical sensors for high-precision measurements, often used in specialized applications.
11.How do I troubleshoot issues with my CNC zero probe?
To troubleshoot issues with a CNC zero probe:
- Check Connections: Ensure all electrical connections are secure and correctly grounded.
- Verify Settings: Confirm that the control system’s input/output assignments and parameters are correct.
- Inspect the Probe: Look for any signs of damage or wear on the probe itself.
- Consult the Manual: Refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps and maintenance guidelines.
- Run Diagnostics: Use the CNC machine’s diagnostic tools to check for errors or misalignments in the probe system.
By understanding and following these guidelines, you can effectively install, configure, and maintain a CNC zero probe to enhance your machining operations.
แคทรีน่าที่
วิศวกรฝ่ายขายเครื่องกลที่มีประสบการณ์มากกว่า 10 ปีในอุตสาหกรรมการผลิต มีทักษะในการพัฒนาและดำเนินกลยุทธ์การขาย สร้างความสัมพันธ์กับลูกค้า และปิดการขาย มีความเชี่ยวชาญในเครื่องมือการขายและการตลาดที่หลากหลาย รวมถึงซอฟต์แวร์ CRM เครื่องมือสร้างโอกาสในการขาย และโซเชียลมีเดีย ฉันสามารถทำงานได้อย่างอิสระและเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของทีมเพื่อให้บรรลุเป้าหมายและวัตถุประสงค์การขาย มุ่งมั่นพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องและเรียนรู้เทคนิคการขายใหม่ๆ