Email: katrina@qidumetro.com Phone: (+86) 134 1323 8643
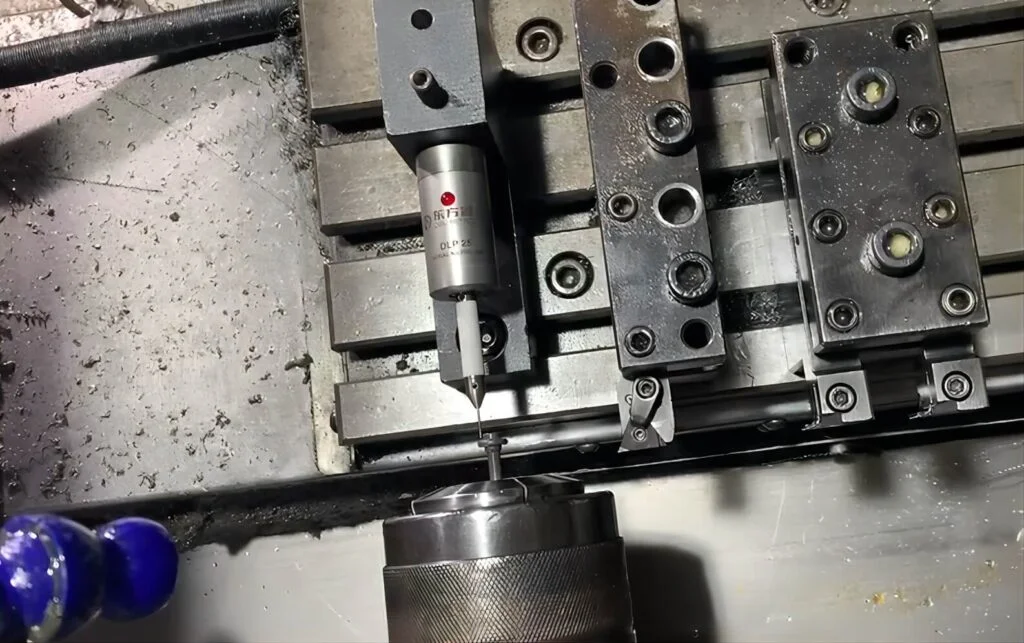
Integrating 3D probing technology into CNC machines has significantly enhanced the manufacturing industry’s capabilities. Combining the precision of 3D probes with CNC machining, these machines offer unmatched accuracy and efficiency. This guide outlines the essential steps to set up and optimize your 3D probe CNC machine for peak performance and productivity.
Installing and Calibrating the Components
The first step in setting up your 3D probe CNC is to ensure all components are properly installed and calibrated. Key components include the probe, spindle, and linear scales. Following the manufacturer’s installation and calibration guidelines is crucial to ensure the machine operates at its best. Regular maintenance and inspections are also vital to prevent any issues that could compromise the machine’s accuracy and reliability.
Configuring the Control Software
After installing and calibrating the hardware, the next step is to configure the machine’s software. This involves setting parameters such as probe type, diameter, and length, as well as inputting calibration data. The software must also be tailored to the specific materials and processes you’ll be working with. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation and seeking expert advice can help ensure optimal software configuration.
Creating a 3D Model
With the software set up, you need to create a 3D model of the part to be produced. This is typically done using CAD software, which allows you to define all necessary dimensions and features. Once completed, the model is imported into the CNC machine’s software and converted into G-code, the machine’s programming language.
Inspecting the G-Code
The G-code file, which directs the machine’s operations, must be meticulously inspected. It should include precise instructions for measuring the part’s dimensions and making any necessary adjustments to the machine’s positioning. Additionally, it should contain detailed commands for the machine’s cutting tools to execute the required machining tasks accurately.
Performing a Test Run
Before commencing the actual machining, it’s essential to perform a test run. This step ensures that all settings are correct and the probe accurately measures the part’s dimensions. During the test run, the machine should probe the part without engaging in any machining operations. Any discrepancies between the measured and actual dimensions must be resolved before proceeding.
Executing the Machining Operations
After successful calibration and a thorough test run, you can begin the actual machining operations. The 3D probe CNC machine will utilize the probe’s measurements to make real-time adjustments to its positioning, ensuring the part is manufactured with the highest precision and accuracy.
Zaključek
Setting up and optimizing a 3D probe CNC machine involves a series of detailed steps: component installation and calibration, software configuration, creating and converting a 3D model, conducting a test run, and performing the machining operations. By diligently following these steps and maintaining the machine properly, manufacturers can leverage 3D probing technology to achieve superior accuracy and efficiency in their production processes.
FAQ: 3D Probe CNC
Understanding how to set up and optimize a 3D probe CNC machine is crucial for leveraging its full potential. Below, we’ve compiled answers to some frequently asked questions to help you get the most out of your 3D probe CNC machine.
1. What is a 3D Probe CNC Machine?
V: What exactly is a 3D probe CNC machine?
A: A 3D probe CNC machine combines the precision of 3D probing technology with the automation and accuracy of CNC machining. It uses a probe to measure the dimensions of a part in three dimensions and then adjusts the machining process based on these measurements to ensure high precision and efficiency.
2. How Does a 3D Probe Work in a CNC Machine?
V: How does the 3D probing technology function within the CNC machine?
A: The 3D probe is a sensor that touches the surface of the part to collect data on its dimensions and geometry. This information is used by the CNC machine to adjust its cutting tools and machining paths in real time, ensuring the part is produced accurately according to the design specifications.
3. What Are the Key Components of a 3D Probe CNC Machine?
V: What are the essential components of a 3D probe CNC machine?
A: The main components include the probe (which gathers dimensional data), the spindle (which holds and rotates the cutting tools), and linear scales (which measure the machine’s movements). Other important parts include the CNC controller, software for processing data and commands, and the cutting tools themselves.
4. How Do I Install and Calibrate the Components?
V: What steps are involved in installing and calibrating a 3D probe CNC machine?
A: Installation involves setting up the probe, spindle, and linear scales according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Calibration is crucial and includes adjusting these components to ensure accurate measurements and operations. Regular maintenance and inspections are necessary to maintain optimal performance.
5. How Do I Configure the Machine’s Software?
V: What is involved in configuring the software for a 3D probe CNC machine?
A: Software configuration includes setting machine parameters such as probe type, diameter, length, and calibration data. You also need to configure the software to accommodate the specific materials and processes you will use. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s documentation and seek expert advice for accurate configuration.
6. How Do I Create a 3D Model for Machining?
V: How can I create a 3D model for use with a 3D probe CNC machine?
A: Use CAD software to design the part, including all necessary dimensions and features. Once the model is created, it can be imported into the CNC machine’s software and converted into G-code, which the machine uses to execute the machining operations.
7. What Is G-Code and How Is It Used?
V: What is G-code, and why is it important?
A: G-code is the programming language used by CNC machines to control their movements and operations. It includes instructions for positioning, probing, and cutting. Carefully inspecting the G-code is essential to ensure it contains all the necessary commands for accurate and efficient machining.
8. Why Is a Test Run Important?
V: Why should I perform a test run before actual machining?
A: A test run helps verify that the machine’s settings are correct and that the probe accurately measures the part’s dimensions. It involves the machine probing the part without performing any cutting operations. Any discrepancies found during the test run can be corrected to prevent errors during the actual machining process.
9. How Do I Optimize the Machining Operations?
V: How can I optimize the actual machining operations with a 3D probe CNC machine?
A: After successful calibration and a test run, proceed with the machining operations. The 3D probe will continuously provide data for real-time adjustments, ensuring the highest precision and accuracy in the production of the part. Properly configuring the machine and maintaining it regularly are key to optimization.
10. How Can I Maintain My 3D Probe CNC Machine?
V: What maintenance practices are recommended for a 3D probe CNC machine?
A: Regular maintenance is vital for optimal performance. This includes routine inspection and calibration of the probe, spindle, and linear scales. Keeping the software updated and performing scheduled cleaning and servicing of the machine will help prevent issues and extend the machine’s lifespan.
Katrina
Mechanical Sales Engineer with 10+ years of experience in the manufacturing industry.Skilled in developing and executing sales strategies, building relationships with customers, and closing deals. Proficient in a variety of sales and marketing tools, including CRM software, lead generation tools, and social media. I'm able to work independently and as part of a team to meet sales goals and objectives. Dedicated to continuous improvement and learning new sales techniques.