Email: [email protected] Phone: (+86) 134 1323 8643
In today’s manufacturing world, achieving consistent quality is essential. Products must meet precise specifications for functionality, safety, and regulatory compliance. Quality control plays a vital role here. It involves inspections and tests throughout manufacturing to ensure the final product meets set standards.
Enter CNC tool probes – innovative advancements that are changing how manufacturers approach quality control. These intelligent tools, integrated with CNC machines, offer a comprehensive and automated solution for improving precision, streamlining processes, and ensuring consistent quality throughout production runs.
Understanding CNC Tool Probes
The Technology Behind CNC Tool Probes
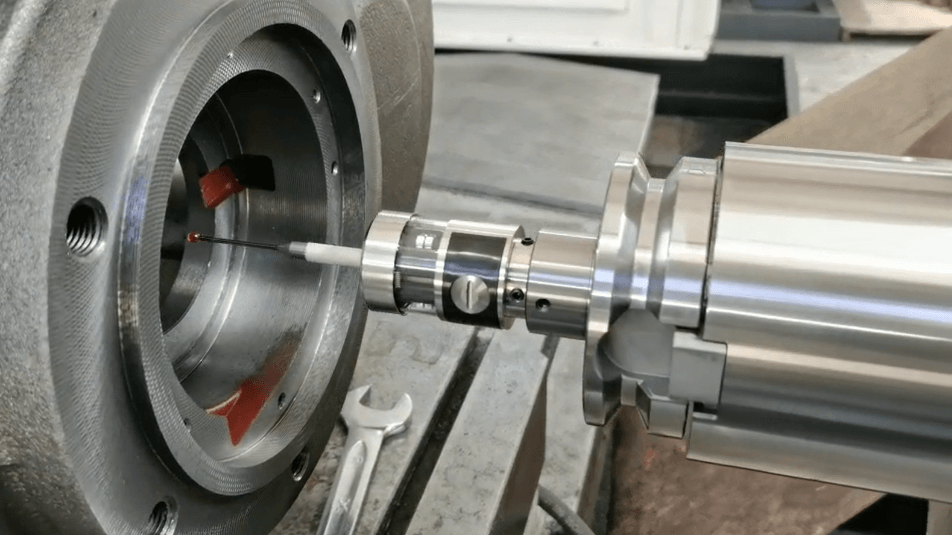
CNC tool probes are essentially specialized sensors attached to a CNC machine’s toolchanger. They come in various types, each suited to specific applications:
- Touch trigger probes: These probes use a spring-loaded mechanism that triggers a signal upon contact with the workpiece.
- Non-contact probes: These probes use technologies like lasers or eddy currents to measure distance without physically touching the workpiece.
- Vision probes: Equipped with cameras, these probes capture images of the workpiece and analyze them for dimensional accuracy.
Regardless of the type, all CNC tool probes connect to the CNC control unit. This allows for two-way communication, enabling the probe to gather data and transmit it to the control unit for further processing and adjustments.
How CNC Tool Probes Work and Their Function in Machining Processes
The functionality of CNC tool probes can be broken down into three key areas:
- Automated Tool Setting and Offset:Before machining begins, the probe automatically measures the tool length and diameter. This data is used by the CNC control unit to adjust for any tool wear or variations, ensuring the programmed machining path is accurate.
- Workpiece Setup and Verification:The probe can locate reference points on the workpiece, verifying its position and orientation within the machine. This eliminates manual setup errors and guarantees machining occurs in the correct location.
- In-Process Inspection and Monitoring:During machining, the probe can be used to measure critical dimensions of the workpiece at various stages. This allows for real-time adjustments and prevents the production of defective parts.
By automating these tasks, CNC tool probes significantly enhance the accuracy and consistency of the entire machining process.
Benefits of Using CNC Tool Probes for Quality Control
CNC tool probes offer a multitude of advantages for quality control:
- Improved Precision and Accuracy:Automatic tool setting and in-process inspection minimize human error, leading to consistently precise parts that meet tight tolerances.
- Reduced Scrap Rates:Early detection of potential issues during machining prevents the production of scrap parts, saving time and material costs.
- Enhanced Process Efficiency:Automating tasks like tool setting and part verification streamlines the overall machining process, leading to increased production throughput.
- Simplified Quality Documentation:Data collected by the probe can be easily stored and documented, providing a clear audit trail for regulatory compliance.
- Reduced Operator Dependence:Automating QC tasks reduces dependence on skilled personnel, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks.
Achieving Unprecedented Precision with CNC Tool Probes
CNC tool probes eliminate the human element from critical tasks like tool setting and part verification. This translates to unmatched precision in the machining process:
- Automatic Tool Offset:Manual tool setting is prone to human error. CNC tool probes automatically measure tool length and diameter, eliminating inconsistencies.
- Real-Time Compensation for Tool Wear:As tools wear during machining, their dimensions change slightly. CNC probes can detect these minute changes and automatically adjust tool offsets, ensuring consistent machining accuracy throughout the tool life.
- Precise Workpiece Setup:The probe’s ability to locate reference points on the workpiece guarantees accurate positioning within the machine’ This eliminates potential errors caused by manual setup procedures.
Improved Accuracy and Consistency in Manufacturing
The improved accuracy achieved with CNC tool probes translates directly to benefits across manufacturing:
- Reduced Rework and Scrap:Consistent machining accuracy minimizes the production of parts that deviate from specifications, leading to less rework and fewer scrapped parts.
- Improved Product Quality:With higher precision, manufacturers can create products with tighter tolerances and superior functionality.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation:Consistent quality builds trust and customer satisfaction, ultimately leading to a stronger brand reputation.
Optimizing Efficiency through CNC Tool Probes
CNC tool probes not only enhance quality but also streamline the entire quality control process:
- Automated In-Process Inspection:Traditional QC procedures often involve stopping the machine and manually measuring parts at various stages. CNC probes automate these inspections, eliminating downtime and allowing for continuous machining.
- Reduced Reliance on Manual Gauges:Probes eliminate the need for manual measurements with potentially variable accuracy. This reduces dependence on skilled inspectors and associated labor costs.
- Improved Data Collection and Analysis:CNC probes collect real-time data on tool wear, workpiece dimensions, and other critical parameters
This data can be analyzed to identify trends, predict potential issues, and continuously improve the machining process.
Case Studies Demonstrating Time and Cost Savings with CNC Tool Probes
The efficiency gains offered by CNC tool probes are well documented:
- A machine shop reported a 30% reduction in setup times by automating tool setting and workpiece verification with CNC probes.
- Another study showed a 25% decrease in scrap rates due to early detection of machining errors through in-process inspection with probes.
These examples highlight the significant time and cost savings achievable through streamlined QC processes facilitated by CNC tool probes.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements with CNC Tool Probes
In today’s manufacturing environment, adhering to industry standards and regulations is crucial. CNC tool probes play a vital role in ensuring compliance:
- Accurate and Traceable Data:The data collected by CNC probes during machining is time-stamped and stored electronically. This creates an auditable trail that demonstrates adherence to specific quality standards.
- Reduced Risk of Non-Compliance:By minimizing human error and ensuring consistent quality, CNC probes help manufacturers avoid the risk of producing parts that fail to meet regulatory requirements.
- Improved Process Control:The data collected by probes allows for continuous process monitoring and improvement. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to quality and facilitates regulatory compliance audits.
Importance of Data Accuracy and Traceability in Quality Assurance
Data accuracy and traceability are fundamental principles of modern quality assurance practices. CNC tool probes provide both:
- Accurate Data Collection:Unlike manual measurements, which are susceptible to human error, CNC probes provide precise and consistent data.
- Electronic Time-Stamped Records:The data collected by the probes is electronically stored and time-stamped, creating an irrefutable record of the machining process.
This combination of accuracy and traceability ensures manufacturers can confidently demonstrate their commitment to quality and meet the demands of regulatory bodies.
Overcoming Challenges and Maximizing Benefits
Addressing Common Issues and Maximizing CNC Tool Probe Benefits
While CNC tool probes offer significant advantages, some challenges need to be addressed:
- Initial Investment Costs:The upfront cost of purchasing and installing CNC tool probes can be a deterrent for some manufacturers.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Integrating CNC probes with existing CNC machines and quality control systems might require additional investment and technical expertise.
- Operator Training:Successful implementation requires proper training for operators on how to use and interpret the data generated by the probes.
Strategies to Overcome Obstacles and Optimize the Benefits of CNC Tool Probes
Here are some strategies to overcome these challenges and maximize the benefits of CNC tool probes:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis:Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI) considering factors like reduced scrap rates, improved efficiency, and enhanced quality.
- Phased Implementation:Consider a phased implementation approach, starting with a single machine or process to demonstrate the value proposition before scaling up.
- Leverage Manufacturer Support:Many CNC probe manufacturers offer comprehensive training and support services to ensure smooth integration and optimal utilization of their products.
By carefully considering these challenges and implementing appropriate strategies, manufacturers can unlock the full potential of CNC tool probes and achieve a significant competitive edge through superior quality control practices.
Common Questions About CNC Tool Probes in Quality Control
A: How do CNC tool probes contribute to reducing production errors?
CNC tool probes address several root causes of production errors:
- They eliminate human error in tool setting and workpiece setup.
- They enable real-time detection of tool wear and potential machining issues.
- They provide accurate and traceable data for continuous process improvement.
By minimizing these factors, CNC tool probes significantly reduce the likelihood of producing defective parts.
B: Can CNC tool probes be integrated with existing quality control systems?
Yes, CNC tool probes can be integrated with most existing quality control systems. Many probe manufacturers offer software solutions that facilitate data communication and integration with popular QC software packages.
C: What are the key factors to consider when selecting a CNC tool probe for quality control purposes?
Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a CNC tool probe:
- Type of probe:Choose the probe type (touch trigger, non-contact, or vision) that best suits your specific application and machining environment.
- Compatibility:Ensure the probe is compatible with your CNC machine’s control unit and software.
- Accuracy and Repeatability:Consider the probe’s specified accuracy and repeatability to ensure it meets the required tolerances for your parts.
- Trigger Force and Sensitivity:Select a probe with appropriate trigger force and sensitivity for your workpiece material and machining operations.
- Environmental Considerations:If your machining environment involves coolant, dust, or vibrations, choose a probe with proper sealing and durability features.
By carefully evaluating these factors and consulting with a qualified CNC probe supplier, you can select the ideal tool to optimize your quality control processes.
Conclusion
CNC tool probes represent a transformative technology for modern quality control practices. They offer a compelling combination of benefits:
- Enhanced precision through automation and real-time adjustments
- Streamlined workflows with reduced downtime and reliance on manual processes
- Improved data collection and analysis for continuous quality improvement
While some initial investment and planning might be required, the long-term benefits of CNC tool probes make them a worthwhile investment for manufacturers seeking to excel in today’s competitive landscape. As quality standards continue to rise and manufacturing processes become more complex, CNC tool probes are poised to play an increasingly critical role in ensuring:
- Consistent quality across production runs
- Reduced waste and improved efficiency
- Regulatory compliance in diverse manufacturing sectors
By embracing this innovative technology, manufacturers can gain a significant competitive edge and deliver superior quality products that meet the ever-evolving demands of the market.
Katrina
Mechanical Sales Engineer with 10+ years of experience in the manufacturing industry.Skilled in developing and executing sales strategies, building relationships with customers, and closing deals. Proficient in a variety of sales and marketing tools, including CRM software, lead generation tools, and social media. I'm able to work independently and as part of a team to meet sales goals and objectives. Dedicated to continuous improvement and learning new sales techniques.