Email: katrina@qidumetro.com Phone: (+86) 134 1323 8643
In the world of manufacturing, achieving pinpoint accuracy is essential. Every machined component, every assembled part, relies on precise measurements to function flawlessly. Enter Measurement Touch Probes, a game-changing technology that injects a new level of precision into the manufacturing process. This article dives into the world of these sensors, exploring their types, functionalities, and the remarkable accuracy they deliver.
What are Measurement Touch Probes?
A Measurement Touch Probe is an ingenious device employed in CNC machining. Imagine a highly sensitive detector mounted onto a CNC machine’s tool holder. This probe acts like a digital finger, making physical contact with the workpiece to gather crucial dimensional data. This data is then fed back to the CNC controller, enabling real-time adjustments and optimizations during the machining process.
Different Types of Measurement Touch Probes
The diverse landscape of Measurement Touch Probes offers a solution for nearly every CNC application. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
- Single-axis touch trigger probe:This workhorse features a spring-loaded stylus that triggers a signal upon contact with the workpiece. It excels in measuring basic dimensions like lengths, widths, and depths.
- Multi-axis touch trigger probe:This advanced probe boasts the ability to measure along multiple axes (X, Y, and Z). This allows for intricate contouring and the acquisition of complex 3D data points.
- Non-contact touch probe:Unlike its trigger counterparts, this sensor utilizes sensors like lasers or eddy currents to detect proximity to the workpiece. Ideal for delicate surfaces or applications requiring continuous measurement without physical contact.
- Tool setter touch probe:This specialized sensor automates tool length and diameter setting, streamlining the setup process and minimizing human error.
- Broken tool detection probe:This probe serves as a guardian angel, safeguarding against costly errors. It can identify broken or damaged tools before they inflict harm on the workpiece.
How Does a Measurement Touch Probe Ĉu labori?
The functionality of a Measurement Touch Probe is deceptively simple yet remarkably effective. Here’s a glimpse into its operation:
- Programming:The CNC programmer defines specific points on the workpiece’s surface for the sensor to contact. These points are meticulously programmed into the CNC controller.
- ProbeActuation: The CNC program instructs the machine to move the sensor towards the designated point on the workpiece.
- Sensing Contact:Upon contact with the workpiece, the chosen sensing mechanism (trigger, laser, etc.) within the sensor generates a signal.
- Data Acquisition:This signal relays the precise location of contact to the CNC controller.
- Real-time Adjustments:The CNC controller interprets the data and can perform adjustments such as tool offset correction or initiate pre-programmed actions based on the acquired measurements.
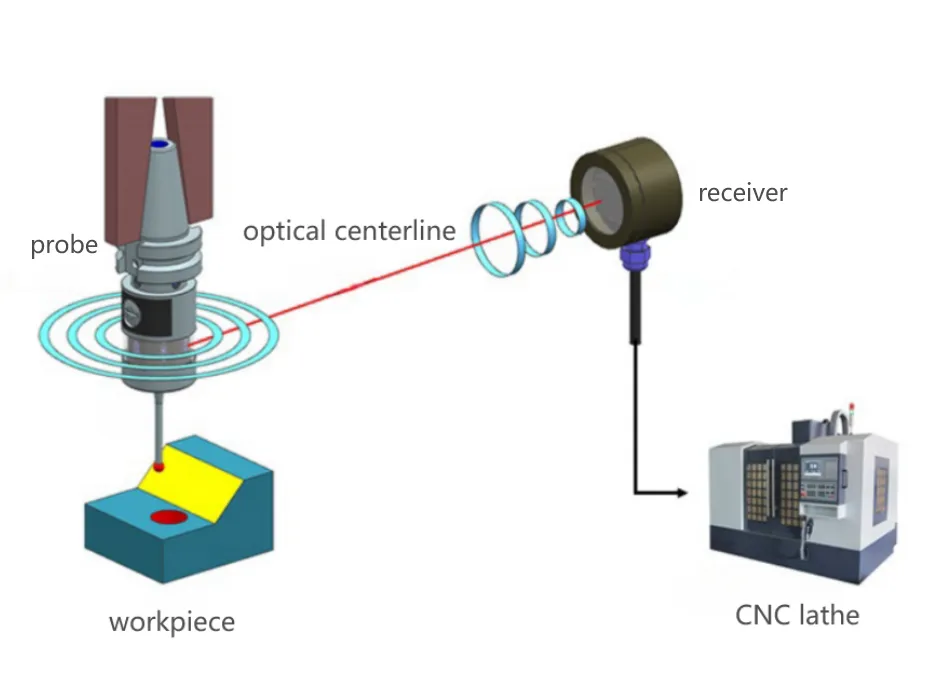
La Avantaĝoj de Measurement Touch Probes
Measurement Touch Probes boast several key characteristics that make them invaluable assets in the CNC machining arena:
- High Accuracy:Modern touch probes deliver exceptional precision, often achieving tolerances within microns. This translates to consistently high-quality parts that meet rigorous specifications.
- Versatility:The variety of touch probe types caters to a broad spectrum of machining applications. Whether it’s simple dimension verification or intricate 3D contouring, there’s a sensor suited for the task.
- Ripeteblo:Probes provide consistent and repeatable measurements, minimizing human error and ensuring consistent part quality throughout production runs.
- Aŭtomatigo:Probes facilitate automated in-process inspection, eliminating the need for manual measurement checks and significantly reducing setup times.
- Reduced Costs:The enhanced accuracy and efficiency offered by touch probes lead to reduced scrap rates, minimized rework, and streamlined production processes, ultimately lowering manufacturing costs.
The Functions of Measurement Touch Probes
Measurement Touch Probes fulfill a multitude of crucial functions within the CNC machining workflow:
- Workpiece Setup and Offset Correction:Prior to machining, the probe sensor precisely locates the workpiece within the machine’s work envelope and sets tool offsets. This ensures the CNC program accurately references the workpiece’s actual position.
- In-Process Inspection:Throughout the machining process, the sensor can verify critical dimensions, detect potential errors, and trigger corrective actions if needed. This real-time feedback loop guarantees part quality and prevents costly mistakes.
- Agordo de Longo kaj Diametro de Ilo:Tool setter touch probe automate the process of setting tool length and diameter, eliminating manual adjustments and enhancing setup speed and consistency.
- Detekto de Rompita Ilo:These specialized touch probe safeguard against unforeseen tool breakage by detecting damaged tools before they inflict harm on the workpiece, minimizing downtime and potential machine damage.
- Data Acquisition for Complex Machining:For intricate 3D machining tasks, sensors can gather a wealth of data points, enabling the creation of highly accurate tool paths.
The Accuracy of Measurement Touch Probe
The importance of accuracy in Measurement Touch Probes cannot be overstated. Several factors contribute to this precision:
- Stylus Design:The stylus, the tip that makes contact with the workpiece, plays a critical role. High-quality styli are crafted from materials like tungsten carbide or ruby, renowned for their hardness and durability. They are also meticulously machined to maintain a consistent shape and size, minimizing measurement errors.
- Signal Processing:The electronic circuitry within the sensor amplifies and filters the signal generated upon contact. Advanced filtering techniques eliminate noise and ensure a clear, precise signal is transmitted to the CNC controller.
- Calibration:Regular calibration is essential to maintain optimal accuracy. This process involves using a reference sphere of known dimensions to verify the sensor’s triggering point and make any necessary adjustments.
The combined effect of these factors allows Measurement Touch Probes to achieve exceptional precision. Typical tolerances range from microns in high-end models to tens of microns in more basic probes. This level of accuracy surpasses what can be consistently achieved through manual measurement techniques, significantly reducing human error and enhancing manufacturing repeatability.
The Future of Precision
As machining technology continues to evolve, Measurement Touch Probes will undoubtedly remain at the forefront, ensuring ever-increasing levels of precision and automation in the world of manufacturing. We can expect to see advancements in areas like:
Katrina
Mechanical Sales Engineer with 10+ years of experience in the manufacturing industry.Skilled in developing and executing sales strategies, building relationships with customers, and closing deals. Proficient in a variety of sales and marketing tools, including CRM software, lead generation tools, and social media. I'm able to work independently and as part of a team to meet sales goals and objectives. Dedicated to continuous improvement and learning new sales techniques.

