Email: katrina@qidumetro.com Phone: (+86) 134 1323 8643
In the realm of CNC machining, precision reigns supreme. Every cut, every drill, and every mill relies on the exact positioning of the cutting tool for flawless results. This is where CNC tool setters come into play, acting as the silent guardians of accuracy and efficiency.
Understanding the Significance of CNC tool setters
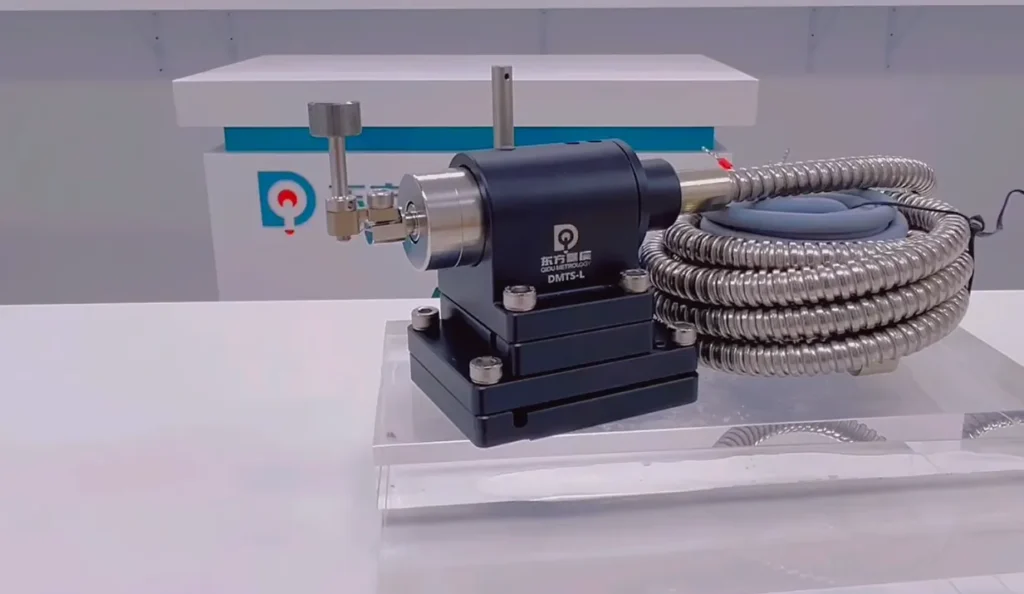
CNC tool setters are specialized sensors that automate the process of setting tool length and diameter offsets within a CNC machine. Traditionally, this task involved manual measurements and test cuts, a process prone to human error and time-consuming. Tool setters eliminate this human element, establishing a new standard for accuracy and repeatability.
Importance of CNC tool setters in CNC Machining
The significance of tool setters is multifaceted. Let’s delve deeper into their impact:
A: Enhancing Precision with CNC tool setters
Even the slightest discrepancy in tool length can have disastrous consequences on the final product. CNC tool setters guarantee accurate tool positioning by automatically measuring the length and offsetting it within the CNC program. Besides, the tool setters elevate machining precision in several key ways:
- Eliminating Human Error:Manual tool setting is prone to mistakes. Tool setters automate the process, ensuring consistent and accurate tool length and diameter measurements. This minimizes human error as a factor affecting precision.
- Repeatability:Tool setters provide repeatable measurements. Each time a tool is measured, the setter delivers the same result, reducing inconsistencies in tool positioning and enhancing overall machining accuracy.
- Temperature Compensation:Slight temperature fluctuations can impact tool length. Some tool setters incorporate temperature sensors to account for these variations and adjust offsets accordingly, maintaining precise tool positioning.
- Tool Wear Detection:Certain tool setters can detect tool wear by measuring minuscule changes in tool length or diameter. Early detection of wear allows for preventative tool changes, preventing inaccuracies caused by dull or damaged tools.
B: Impact of High-Frequency Tool Adjustments
Modern CNC machining often involves frequent tool changes, particularly in complex projects. Each tool change necessitates resetting the tool offset. CNC tool setters automate this process, significantly reducing setup times and allowing for faster production cycles.
The Functionality of CNC tool setters
Understanding how CNC tool setters work sheds light on their effectiveness:
A: Operating Principles of CNC tool setters
A typical CNC tool setter is a touch probe triggered by physical contact with the tool tip. The probe transmits a signal to the CNC controller upon contact, indicating the exact tool position. This information is then used to automatically calculate and set the tool offset within the program.
B: Benefits of Incorporating CNC tool setters
The advantages of implementing CNC tool setters are numerous:
- Enhanced Precision and Reduced Scrap:Eliminate manual tool offset calculations and the possibility of human error during setup. This leads to more consistent tool positioning and part dimensions, minimizing scrapped parts due to machining inconsistencies.
- Faster Setup Times:Manual tool offset setting can be quite time-consuming. Tool setters automate this process, significantly reducing setup times and allowing for quicker operation of your CNC machine.
- Boosted Productivity:Reduced setup times and minimized scrap rates through the use of tool setters can significantly improve your overall machining productivity. You’ll be able to produce more parts in less time, enhancing profitability.
- Reduced Reliance on Skilled Operators:Tool setters remove some of the expertise required for manual tool setting. This can make your machining operation less reliant on highly skilled operators, and simplifies training new employees.
- Improved Machine Protection:By ensuring accurate tool offsets, tool setters can help to prevent crashes and other machine damage caused by incorrect tool positioning.
- Extended Tool Life:Reduced tool wear and tear through accurate positioning and minimized setup times can lead to extended tool life and reduced tooling costs.
- Enhanced Data Collection and Monitoring:Certain tool setters offer functionalities for data collection and monitoring of tool wear and performance. This valuable information can be used for preventative maintenance and optimizing machining processes.
Improving Efficiency and Quality with CNC tool setters
The impact of CNC tool setters extends beyond accuracy, directly influencing the efficiency and quality of CNC machining:
A: How CNC Tool Setters Streamline CNC Machining Processes
By automating tool setting and minimizing setup times, CNC tool setters significantly accelerate production cycles. This translates to increased output and improved overall workflow within the machine shop.
B: Ensuring Consistency and Reliability in Production
Automated tool setting guarantees consistent tool offsets across all production runs, eliminating human inconsistencies and leading to a higher degree of product quality and repeatability.
The Future Trends of the CNC tool setter
The future of CNC machining is headed towards greater automation, efficiency, and precision. This trend is sure to influence the development of CNC tool setters as well. Here are some potential future trends we can expect to see:
- Increased Integration with Sensors and AI:CNC tool setters will likely become more sophisticated, incorporating additional sensors to gather data about tool health, vibration, and wear. This data can then be fed into AI algorithms to predict tool failure and optimize machining processes.
- Self-learning and Automatic Calibration:Tool setters could become self-learning, automatically calibrating themselves based on past data and real-time sensor readings. This would eliminate the need for manual intervention and ensure consistent accuracy.
- Wireless Communication and Connectivity:The rise of Industrial IoT (IIoT) will likely see tool setters equipped with wireless communication capabilities. This would allow for real-time data exchange with machine controllers and other shop floor devices, enabling better process monitoring and optimization.
- Universal Tool Setting Systems:Currently, different CNC machines may require specific tool setter models. In the future, there could be a move towards more universal tool setting systems that can be easily adapted to various machines, reducing complexity and costs.
- Focus on preventative maintenance:Tool setters could play a more prominent role in preventative maintenance programs. By continuously monitoring tool health, they can help identify potential issues before they cause costly downtime.
Common Questions about CNC tool setters
Here we address some frequently asked questions about CNC tool setters:
A. What Types of CNC tool setters Are Available in the Market?
There are various types of CNC tool setters, including:
- Touch Trigger:These activate upon physical contact with the tool tip.
- Non-Contact:These utilize sensors like lasers or eddy currents to detect tool position without physical contact.
- In-Spindle:These are integrated directly into the CNC spindle for tool setting within the tool holder.
B. How Can CNC tool setters Improve Production Efficiency?
CNC tool setters streamline setup times by automating tool setting, allowing for faster tool changes and quicker production cycles.By incorporating CNC tool setters into your workflow, you unlock a new level of precision, efficiency, and consistency in your CNC machining operations. These game-changing tools pave the way for a more streamlined and high-quality production environment.
Katrina
Mechanical Sales Engineer with 10+ years of experience in the manufacturing industry.Skilled in developing and executing sales strategies, building relationships with customers, and closing deals. Proficient in a variety of sales and marketing tools, including CRM software, lead generation tools, and social media. I'm able to work independently and as part of a team to meet sales goals and objectives. Dedicated to continuous improvement and learning new sales techniques.